HEALTH
Understanding Melanoma In Situ: What You Need to Know
Melanoma is an extremely serious and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It is caused by the abnormal proliferation of cells called melanocytes that produce pigment. Melanoma is frequently difficult to treat and frequently necessitates severe medical intervention. Melanoma in situ is regarded as the most curable and early stage of the illness. This page explains what melanoma in situ is, how it is diagnosed, and the current treatment choices for patients who have been diagnosed with this condition.
What is Melanoma In Situ?
Melanoma in situ is a form of skin cancer that develops when melanocytes in the skin begin to proliferate abnormally and create a flat, frequently pigmented lesion. This lesion is considered in situ since it has not yet spread to other areas of the body. Melanoma in situ is the earliest stage of melanoma and is frequently highly curable.
What Causes Melanoma In Situ?
Although the actual origin of melanoma in situ is uncertain, UV exposure and genetics are suspected to play a role. Those with a family history of skin cancer and those who spend a great deal of time in the sun are more susceptible to developing this ailment.
How is Melanoma In Situ Diagnosed?
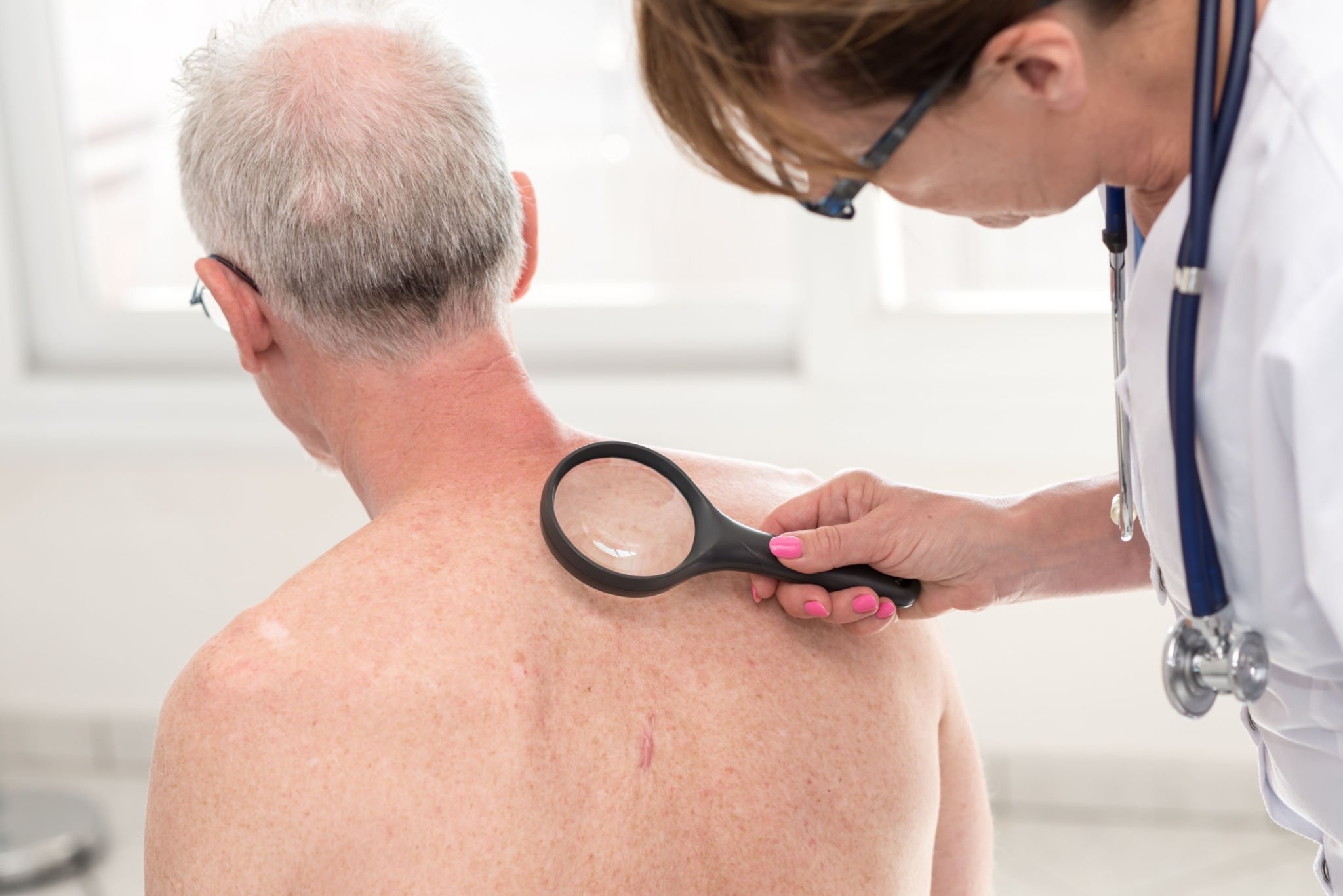
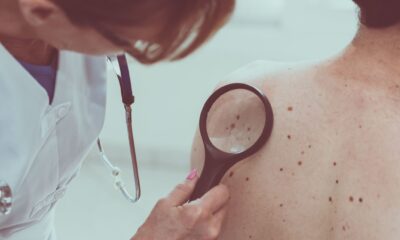
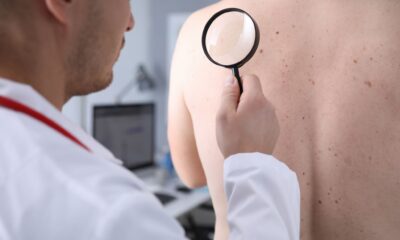
The afflicted skin is routinely biopsied to diagnose melanoma in situ. A little sample of the worrisome lesion is taken and inspected under a microscope during this process. The biopsy will indicate if the lesion is melanoma in situ or another form of skin disorder.
In rare instances, a dermatologist may undertake a visual examination and then use a dermatoscope to inspect the lesion more closely. The dermatoscopy enables the dermatologist to examine the lesion in greater detail for indications of aberrant growth or pigment changes.
Treatment Options for Melanoma In Situ
Typically, melanoma in situ is treated with surgical excision of the afflicted skin. This can be accomplished with a straightforward excision, which entails removing the entire lesion plus a small margin of good skin surrounding it.
In some instances, a more comprehensive surgery, such as a larger excision or a skin graft, may be required to eliminate the lesion. After the lesion has been removed, the patient must return for regular follow-up sessions with the dermatologist to monitor for symptoms of recurrence.
In addition to surgery, various treatments, such as topical creams, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy, may be advised for melanoma in situ. These therapies are intended to lower the chance of the disease spreading to other parts of the body and prevent the disease from recurring.
Preventing Melanoma In Situ
The most effective method for preventing melanoma in situ is to shield the skin from excessive sun exposure. This can be accomplished by wearing protective clothes, applying sunscreen, and seeking shade during the sun’s peak hours.
In addition to protecting your skin from the sun, it is essential to do regular self-exams of your skin. This will enable you to identify any suspicious moles or lesions on your skin and, if necessary, seek medical assistance.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Melanoma in situ is a very treatable form of skin cancer, however, early detection is essential for the best prognosis. If you suspect that you have melanoma in situ, you should seek medical assistance immediately. Your dermatologist can perform a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and advise you on the most effective treatment.
Early therapy may prevent the disease from spreading to other parts of the body.
Is Melanoma In Situ a Serious Condition?
Melanoma in situ, a kind of skin cancer, is a dangerous disorder. However, this stage of melanoma is easier to treat and less likely to result in major consequences than in later stages. It is essential to discover and treat this type of melanoma as early as possible, as early detection and treatment can significantly raise the likelihood of a positive outcome.
How is Melanoma In Situ Different from Other Forms of Skin Cancer?
Melanoma in situ differs from other forms of skin cancer in that it has not yet spread beyond the top layer of skin and is in its initial stage. Other forms of skin cancer, such as invasive melanoma, have penetrated deeper into the skin and surrounding tissues, making them more difficult to cure and more likely to cause severe problems.
Can Melanoma In Situ Spread to Other Parts of the Body?
Melanoma in situ has not yet moved beyond the top layer of skin, hence it is highly unlikely that it will spread to other areas of the body. However, if left untreated, it can progress to a more advanced stage of melanoma that can spread to other organs. This is the reason why early detection and treatment of in situ melanoma is so critical.
What is the Prognosis for Melanoma In Situ?
Assuming early detection and treatment, the prognosis for melanoma in situ is usually favorable. In the majority of instances, surgical removal of damaged skin is effective in treating this illness, and the patient can go on to enjoy a healthy life free of skin cancer.
Can Melanoma In Situ Recur After Treatment?
After therapy, melanoma in situ can return in rare instances. This is why it is essential to regularly monitor your skin for any changes or new moles and to undergo routine skin cancer screenings with your physician. With early discovery and treatment, the likelihood of a positive outcome is significantly boosted.
What Should I Do if I Think I Have Melanoma In Situ?
If you suspect you have melanoma in situ, it is imperative that you consult a doctor immediately. Your doctor can do a biopsy and physical examination to determine the presence of cancer cells and establish a treatment plan to help you recover and prevent the progression of the condition.
Conclusion
Melanoma in situ is a form of skin cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. By learning the fundamentals of this ailment, including its symptoms, causes, and therapies, you can safeguard your loved ones more effectively. Remember to monitor any moles on your skin and to have them examined by a physician if you observe any changes. You can lower your risk of getting this condition and live a healthy, cancer-free life with the proper care and attention.